About This Journal
Horticultural Science and Technology (abbr. Hortic. Sci. Technol., herein ‘HST’; ISSN, 1226-8763), one of the two official journals of the Korean Society for Horticultural Science (KSHS), was launched in 1998 to provide scientific and professional publication on technology and sciences of horticultural area. As an international journal, HST is published in English and Korean, bimonthly on the last day of even number months, and indexed in ‘SCIE’, ‘SCOPUS’ and ‘CABI’. The HST is devoted for the publication of technical and academic papers and review articles on such arears as cultivation physiology, protected horticulture, postharvest technology, genetics and breeding, tissue culture and biotechnology, and other related to vegetables, fruit, ornamental, and herbal plants.



-
Research Article
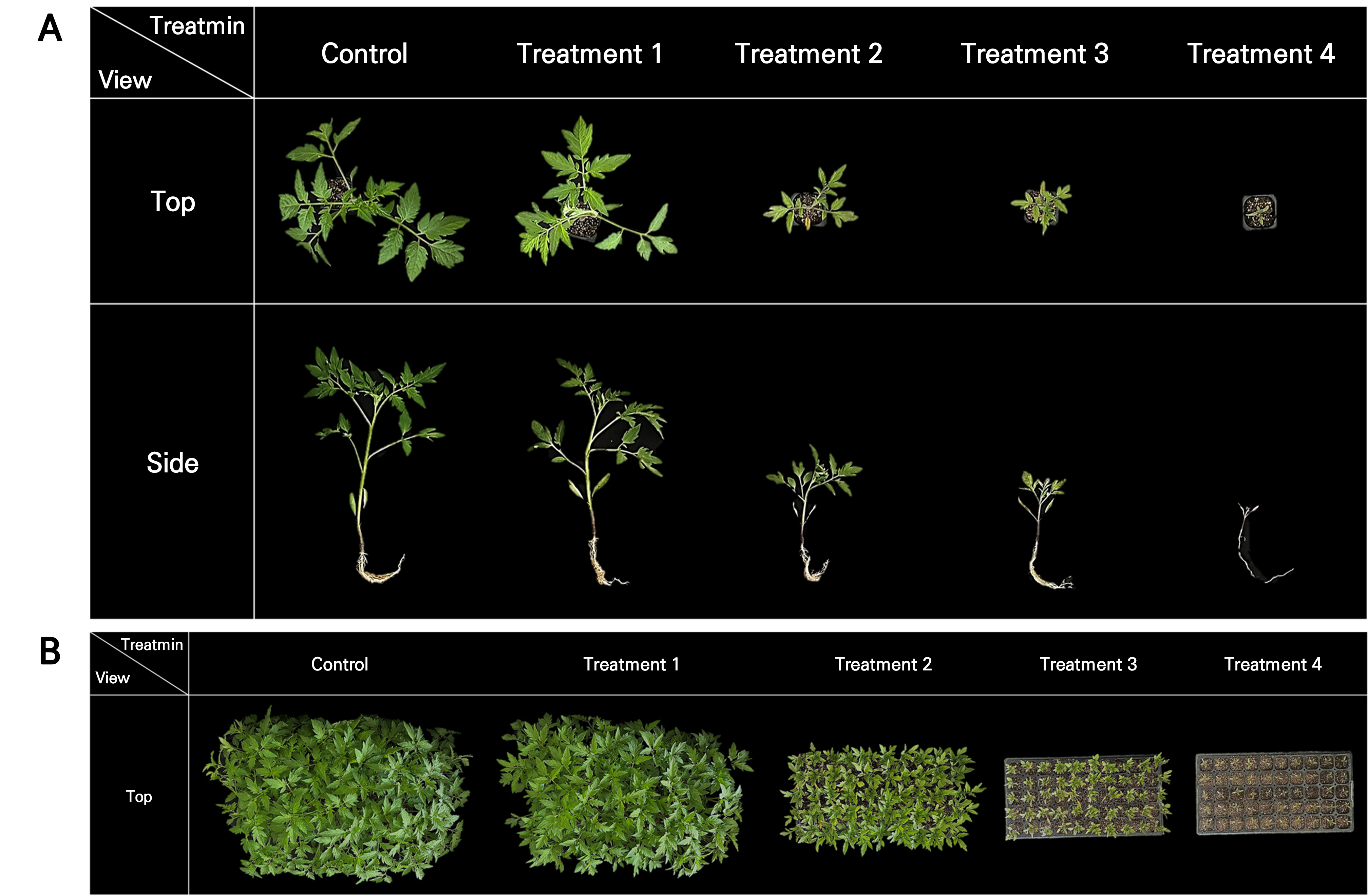

- Detection of Nitrogen and Water-Deficit Stress in Single-plant and Plug-tray Units of Tomato Seedlings using Spectral Imaging
- Solly Kang, Yu Kyeong Shin, Yang Gyu Ku, Yurina Kwack, Jun Gu Lee
- Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging data have recently been used to support research that evaluated specific abiotic stress levels in single-plant units. However, …
- Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging data have recently been used to support research that evaluated specific abiotic stress levels in single-plant units. However, for practical applications in a seedling nursery, assessing abiotic stress levels in plug-tray units is necessary. Therefore, this study aimed to develop techniques for identifying nitrogen and water-deficit-stress levels in tomato seedlings in both single-plant and plug-tray units using spectral imaging. Nitrogen-stress treatments included five levels, as well as a control, whereas water-deficit-stress treatments included two levels: a control and a root-zone drying treatment. Spectral reflectance and vegetation indices were calculated using spectral data for different wavelengths obtained from multispectral or hyperspectral cameras. Correlations between spectral image values (reflectance and vegetation indices) and stress-related substances (chlorophyll, proline, and total nitrogen content) were analyzed. It was possible to evaluate by means of multispectral and hyperspectral imaging the nitrogen-stress levels corresponding to the treatments with a seedling nitrogen content of less than 0.89% as a result of restricting nitrogen nutrients for 26 days. Vegetation indices (normalized difference vegetation index [NDVI], green normalized difference vegetation index [GNDVI], and green chlorophyll index [CIgreen]) calculated from multispectral imaging indicated that nitrogen stress could be detected in the treatment that excluded nitrogen for 16 days, with a nitrogen content of 1.30% or less. For water-deficit stress, it was not possible to detect stress levels using multispectral or hyperspectral data within the 1,000 nm wavelength range. Thus, while nitrogen-stress levels can be practically detected at the plug-tray unit level by means of a multispectral or hyperspectral analysis, detecting water-deficit-stress levels using near-infrared wavelengths below 1,000 nm is difficult. This study demonstrated that multispectral or hyperspectral imaging can be used as a practical means of assessing nitrogen-stress levels in single plants and plug-tray units. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
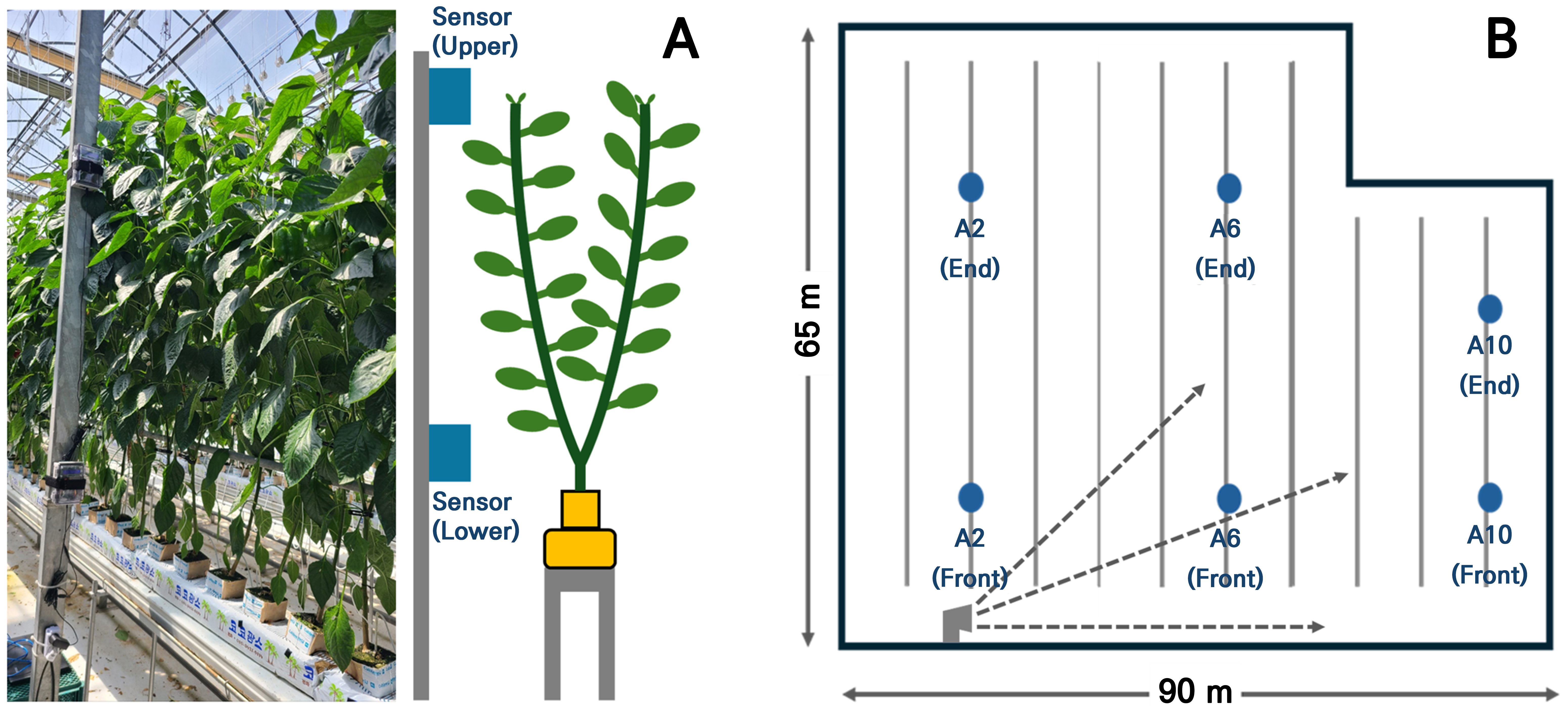
- Comparison of Carbon Dioxide Concentration Distribution and Growth of Bell Pepper according to Locations Within a Multi-span Greenhouse
- Jae Seong Lee, Jong Hwa Shin
- This study was conducted in a 5,200 m2 plastic multi-span greenhouse to establish an efficient carbon dioxide (CO2) supply …
- This study was conducted in a 5,200 m2 plastic multi-span greenhouse to establish an efficient carbon dioxide (CO2) supply strategy by analyzing the distribution of CO2 concentrations according to greenhouse spatial positions and evaluating the effects of CO2 concentration variations on growth rate and yield of paprika. The experiment was carried out from February 21 to July 30, 2024, and supplemental CO2 was not separately supplied during the experiment in order to analyze the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of CO2 within the greenhouse environment. CO2 concentrations were continuously measured at upper and lower positions of the plant canopy using Arduino-based CM1107 sensors. Spatially, the greenhouse was divided into front and rear sections, as well as horizontally into left, central, and right positions. Plant growth parameters, including plant height, stem diameter, number of leaves, number of nodes, leaf area, and fresh weight, were measured weekly and statistically analyzed. The relationship between weekly cumulative daily average CO2 concentration and crop growth rate was evaluated using nonlinear regression modeling. The weekly greenhouse CO2 concentrations notably decreased immediately after sunrise during the early growth stage due to increased photosynthetic activity, while nighttime CO2 levels gradually increased throughout the growth period due to biomass accumulation and associated respiratory CO2 release. Among the positions within the greenhouse, the cumulative daily average CO2 concentration was highest at position A2F, recording 71,478.14 µmol·mol-1, which corresponded to higher fresh weight and leaf area values of 1,015.77 g and 14,416.08 cm2, respectively. The relationship between weekly cumulative daily average CO2 concentration and crop growth rate was best described by a Gaussian peak model (R2 = 0.58). The findings regarding the spatiotemporal distribution of CO2 concentrations within the greenhouse and the resulting crop growth and productivity from this study could serve as fundamental data useful for establishing greenhouse environmental management strategies. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
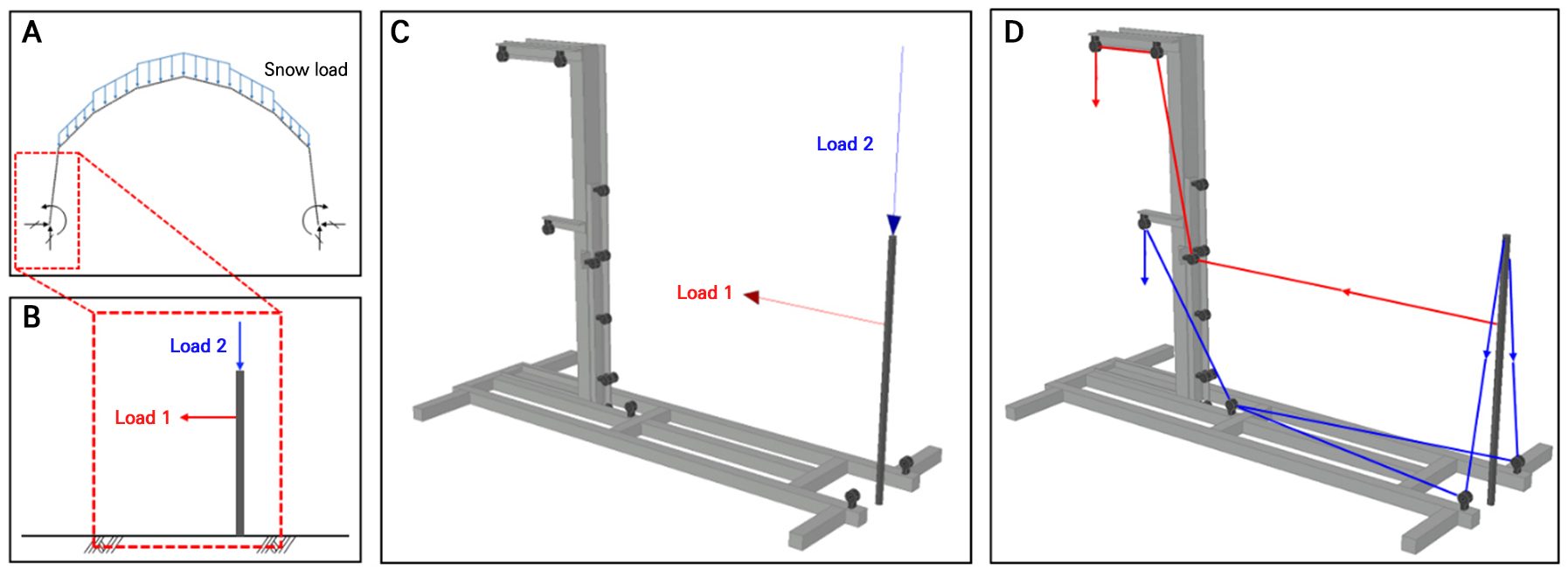
- Reliability Analysis of a Single-span Agricultural Greenhouse Considering the Uncertainty of the Foundation Joint Conditions
- Jeongbae Jeon, Sangik Lee, Solhee Kim, Taegon Kim
- This study investigates the impact of foundation connection uncertainties on the structural reliability of single-span greenhouses by means of a Monte Carlo …
- This study investigates the impact of foundation connection uncertainties on the structural reliability of single-span greenhouses by means of a Monte Carlo simulation. Comparative analyses between fixed-support conditions and those allowing displacement and rotation revealed significant differences in the structural behavior. Under fixed conditions, the maximum von Mises stress remained within the allowable limits (182.6 MPa), with a failure probability of 27.0%. However, with displacement and rotation, the stress exceeded the allowable limits by 50.8% (445.4 MPa), with the failure probability increasing to 50.7%. The results here indicate that the snow unit weight significantly influences structural safety and that the ground-structure interaction is a decisive factor with regard to the structural behavior. Current design standards may be inadequate, particularly given the increasingly extreme environmental conditions caused by climate change. This study suggests incorporating snow unit weight criteria and ground-structure interaction guidelines into greenhouse design standards. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
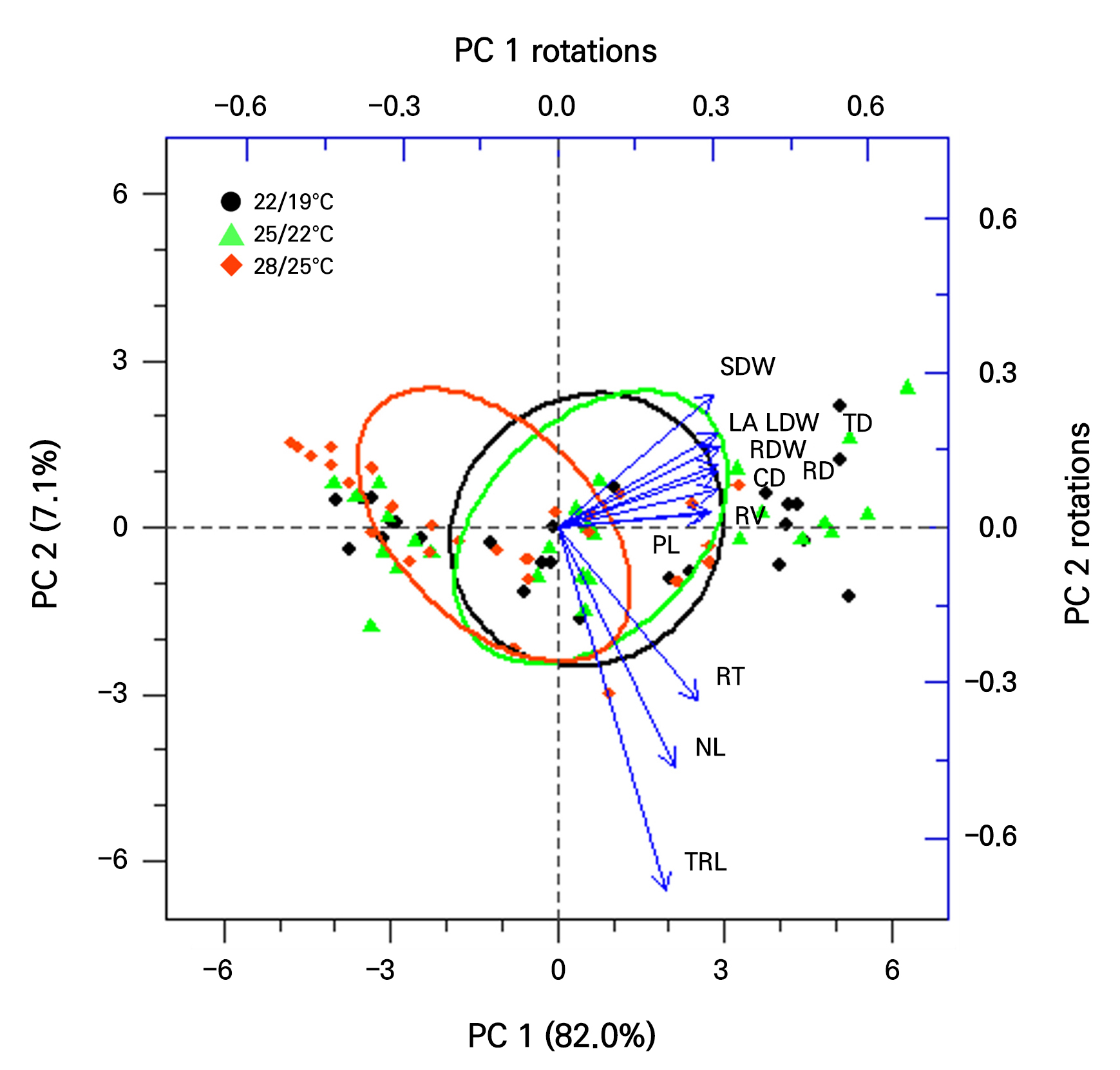
- Effects of Different Temperature Conditions on the Growth and Photosynthesis of Korean Angelica Plug Seedlings in Plant Factories with Artificial Lighting Systems
- Eun Won Park, Jeong Hun Hwang, Hee Sung Hwang, Hyeong Eun Choi, Jeong Kil Koo, Ji Hye Yun, So Yeong Hwang, Seung Jae Hwang
- In this study, we aimed to evaluate the growth characteristics of Korean angelica (Angelica gigas Nakai) seedlings grown under different temperatures …
- In this study, we aimed to evaluate the growth characteristics of Korean angelica (Angelica gigas Nakai) seedlings grown under different temperatures in plant factories with artificial lighting systems (PFALs). The temperatures in the PFALs were maintained at 22/19°C (light/dark), 25/22°C, and 28/25°C, with an alternating 12-hour photoperiod used in each case. Light-emitting diodes (red : green : blue = 7 : 1 : 2) were used as the light sources. Before sowing, Korean angelica seeds underwent two weeks of a cold treatment to break their morphophysiological dormancy. Seeds were sown in 72-cell plug trays, and the resultant seedlings were grown for 60 days to evaluate their growth and development. Additionally, principal component analysis (PCA) was employed to examine the relationships between shoot and root development. It was found that the shoot growth parameters of the crown diameter, leaf area, and leaf dry weight increased at 22/19°C and 25/22°C compared to 28/25°C. Seedlings grown at 22/19°C showed a larger root volume and a significantly higher root : shoot ratio, which was more effective for root development. The net photosynthesis rate tended to increase with a decrease in the temperature. The PCA results confirmed a strong correlation among the petiole length, crown and root diameters, leaf area, leaf and root dry weights, and root volume. These results indicate that Korean angelica seedlings exhibit enhanced root development and net photosynthesis at relatively low temperatures in PFALs. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
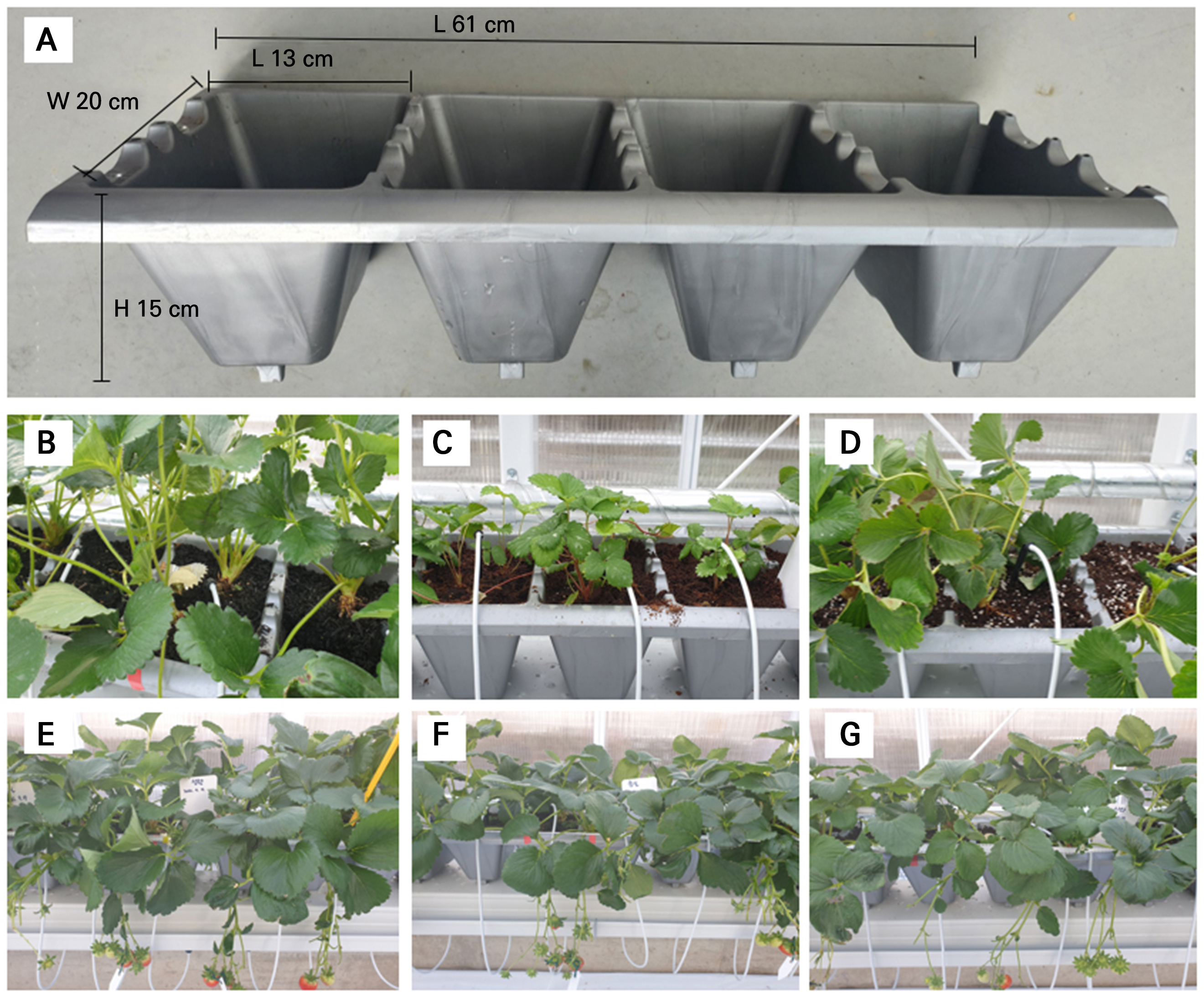

- Effects of Growing Substrates on the Growth, Yield, and Quality of Strawberry Cultivars Grown in a Pot Hydroponic System
- MG Rabbani, Minkyung Kim, Mewuleddeg Zebro, Ki Young Choi
- Substrate composition and cultivar adaptability are key factors influencing strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) growth and fruit quality in hydroponic systems. …
- Substrate composition and cultivar adaptability are key factors influencing strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) growth and fruit quality in hydroponic systems. Pot cultivation enables each plant to grow separately and reduces the risk of disease. Therefore, this study was conducted to evaluate the effects of growing substrates on the growth and quality of strawberry cultivars using a pot hydroponic system. The strawberry cultivars (Sulhyang, Kuemsil, and Santa) were grown in three substrates: biochar (T1), coir dust (T2), and artificial substrate (T3) from September 2022 to March 2023 in a greenhouse. Strawberry seedlings were transplanted into plastic pots, having four cells (L 13 × W 20 × H 15 cm), with two plants per cell. Irrigation was periodically adjusted, and all substrates received equal volumes of nutrient solution. The results showed that growth characteristics, including plant height, leaf width, and crown diameter, were significantly different among the cultivars. The leaf titratable acidity (TA) varied significantly among the cultivars, while leaf electrical conductivity (EC) differed significantly based on the substrates. Fruit number, fruit weight, yield, soluble solid content (SSC), and fruit firmness were higher for Sulhyang in T3 substrate and Kuemsil and Santa cultivars in T2 substrate, whereas they showed the lowest fruit TA. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that leaf EC, leaf TA, fruit SSC, and fruit firmness were strongly associated with Sulhyang cultivated in artificial substrate, as well as Kuemsil and Santa cultivated in coir dust treatments. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
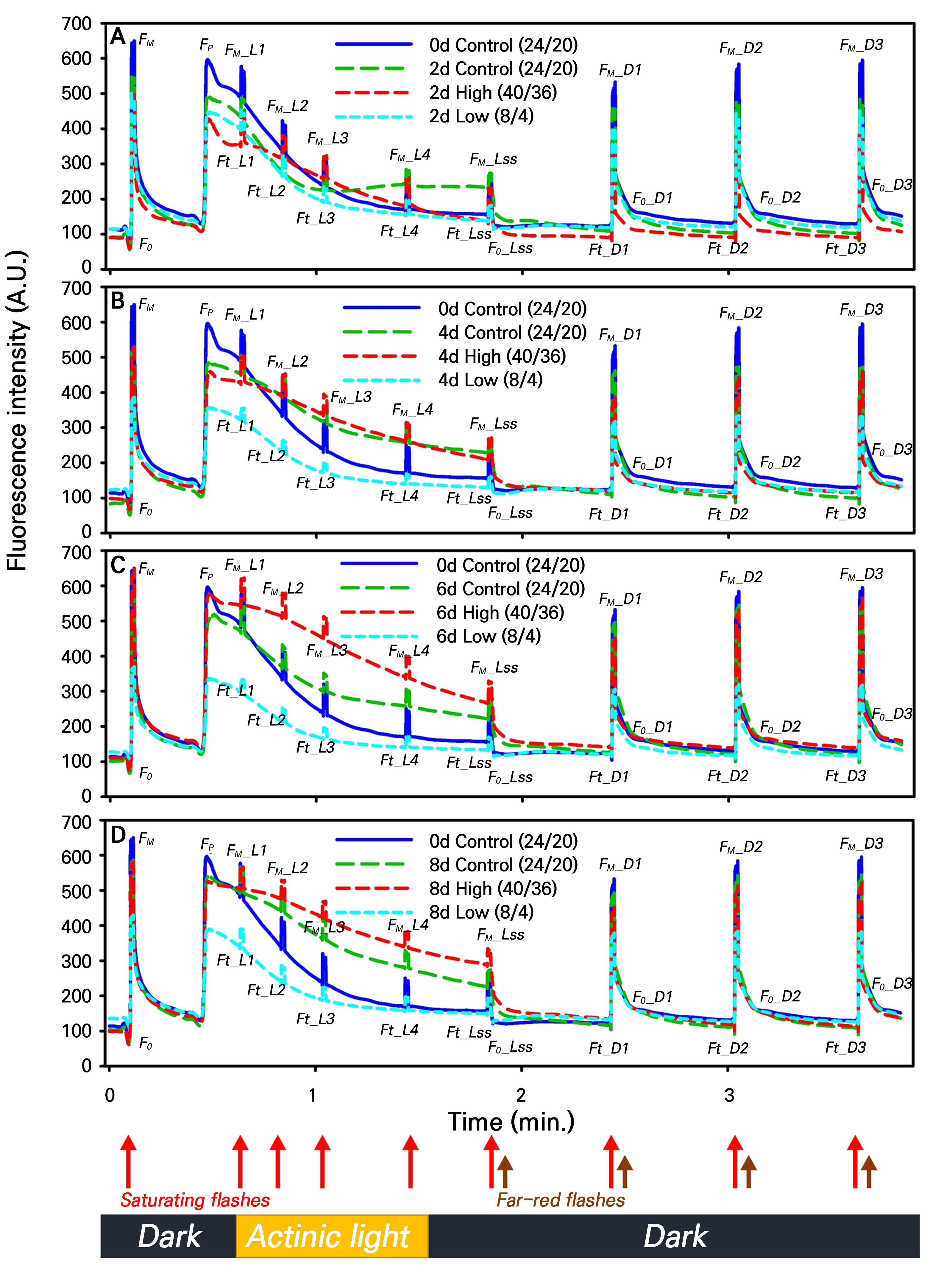
- Differential Physiological and Growth Responses of Lettuce Seedlings to Extreme Thermal Stress Analyzed through Chlorophyll Fluorescence
- Yu Kyeong Shin, Jun Gu Lee
- This study sought to monitor changes in growth parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence (CF) levels, and proline and chlorophyll contents in lettuce seedlings grown …
- This study sought to monitor changes in growth parameters, chlorophyll fluorescence (CF) levels, and proline and chlorophyll contents in lettuce seedlings grown under different temperature conditions. Ten-day-old lettuce seedlings grown under a fluorescent lamp in a closed plant production system having a constant temperature (24/18°C), humidity of 60 ± 3%, and a light period of 14/10 h (day/night) were kept at 24/18°C for three days in a closed chamber under white warm LED lighting at 220 ± 10 µmol∙m-2∙s-1. The seedlings were then grown under different temperature conditions [low: 8/4°C (day/night), control: 24/20°C, and high: 40/36°C] in a closed and controlled plant production system for eight days. The CF parameters, proline amount, and chlorophyll content were measured at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 d after the initiation of the treatment, while the growth parameters (fresh weight, dry weight, leaf length, and hypocotyl length) were measured at the end of the experiment. The quantum yield of nonregulated energy dissipation in PSII [Y(NO)] increased on the second day and then decreased at low temperatures. Non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) and the fluorescence decrease ratio (Rfd) significantly decreased under both high- and low-temperature stress compared to those in the control. Growth parameters were retarded at low temperatures, whereas leaves became dry at high temperatures. The chlorophyll content decreased significantly, whereas the proline content increased only at low temperatures. These results indicate that Y(NO), NPQ, and Rfd can be used to detect temperature stress in lettuce seedlings. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
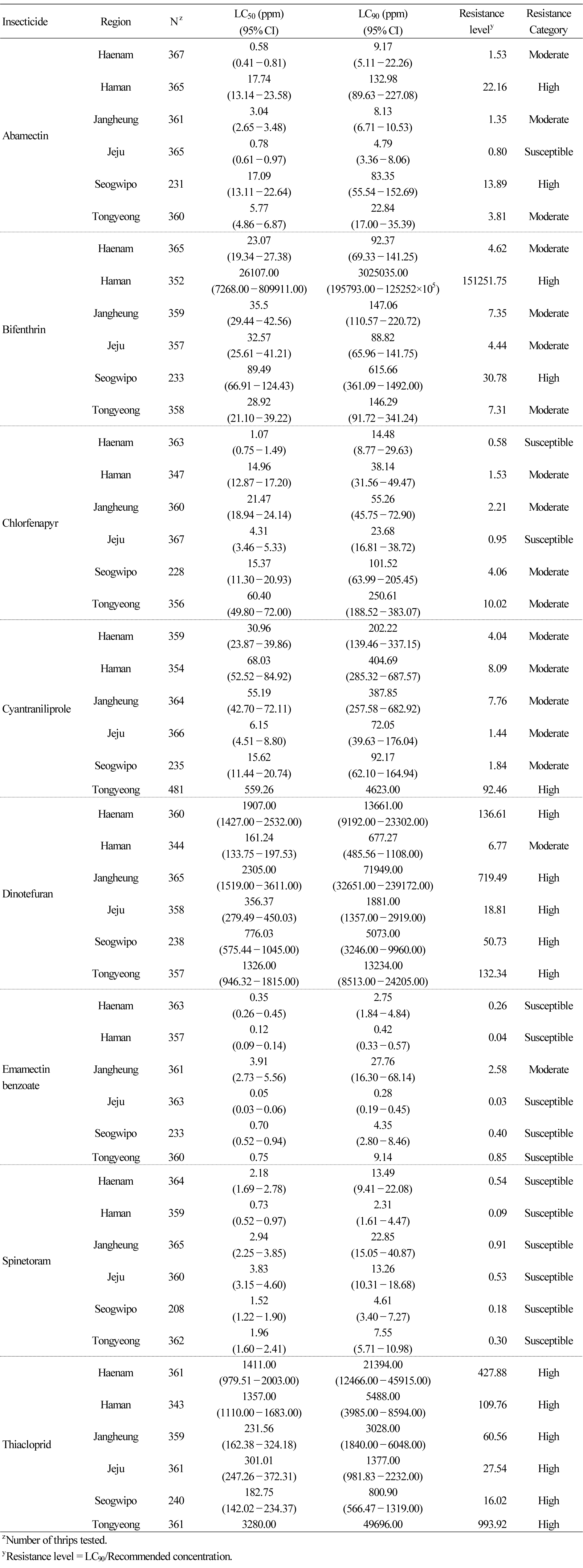
- Insecticide Resistance of Chilli thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) during Mango Cultivation in the Republic of Korea
- Min Jae Kim, Ho Wook Lee, Dae Geon Lee, Kyeong Woo Kim, Rosmery Malory Noli Erquinio, Yi Seul Kim, Abraham Okki Mwamula, Yeon Jin Jang, Dong Woon Lee
- Chilli thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) is a type of serious pest causing a significant damage during mango cultivation in Korea. Control …
- Chilli thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) is a type of serious pest causing a significant damage during mango cultivation in Korea. Control is mainly achieved through the intense application of insecticides, a practice that facilitates the development of insecticide resistance worldwide. We evaluated the resistance of chilli thrips collected from mango cultivation areas in Korea to eight registered insecticides: abamectin 1.8% EC, bifenthrin 2% WP, chlorfenapyr 5% EC, cyantraniliprole 10% SE, dinotefuran 20% WG, emamectin benzoate 2.15% EC, spinetoram 5% SC, and thiacloprid 10% SC. Bifenthrin encountered relatively high resistance, requiring over 4 times the recommended concentration (RC) to produce 90% mortality, in all regions, and high levels of resistance to dinotefuran and thiacloprid were observed in all regions. On the other hand, spinetoram encountered low resistance levels in all regions. Emamectin benzoate was also highly effective, producing LC90 values below the RC in all regions except Jangheung. Chlorphenapyr encountered low resistance levels in Jeju-si and Haenam-gun, but high resistance was recorded in Tongyeong-si. Cyanthraniliprole faced moderate to high resistance in all regions. These findings suggest that there is a need to establish an effective control system for chilli thrips, which would require the continuous monitoring of regional insecticide resistance. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
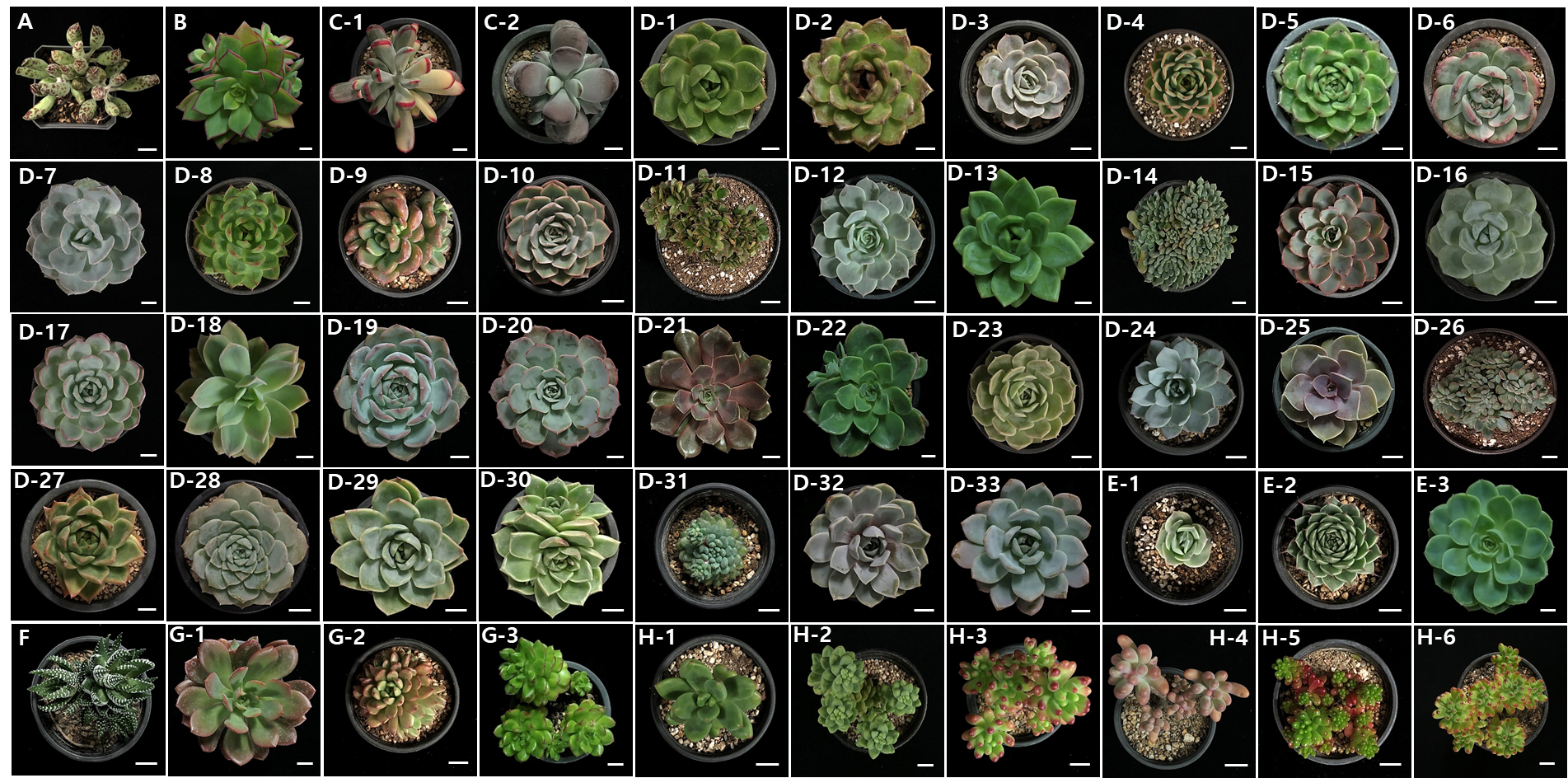

- Comparison of Particulate Matter Trapping Capacities of Commercial Ornamental Succulent Plants
- Ho Jin Lee, Wan Soon Kim
- This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of succulent plants in reducing particulate matter (PM) and investigate how their morphological traits relate …
- This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of succulent plants in reducing particulate matter (PM) and investigate how their morphological traits relate to their PM trapping capacity. In a controlled experiment, 50 cultivars from eight genera within the families Crassulaceae and Asphodelaceae were exposed to PM10 and PM2.5 in a sealed chamber. The amount of PM deposited was quantified using a gravimetric method. The results revealed that succulent plants were more effective in reducing PM than typical foliage plants. Furthermore, the PM trapping capacity varied among cultivars. Cultivars with a greater number of smaller leaves exhibited higher PM-trapping efficiency. Additionally, surface features such as trichomes, tubercles, and pubescence played a significant role in enhancing PM deposition. These findings suggest that the morphological characteristics, particularly the presence of complex surface structures, are crucial for PM reduction. In conclusion, succulents, especially those with well-developed surface structures such as trichomes, have the potential to significantly improve indoor air quality. These plants can be considered valuable air-purifying plants for commercial applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
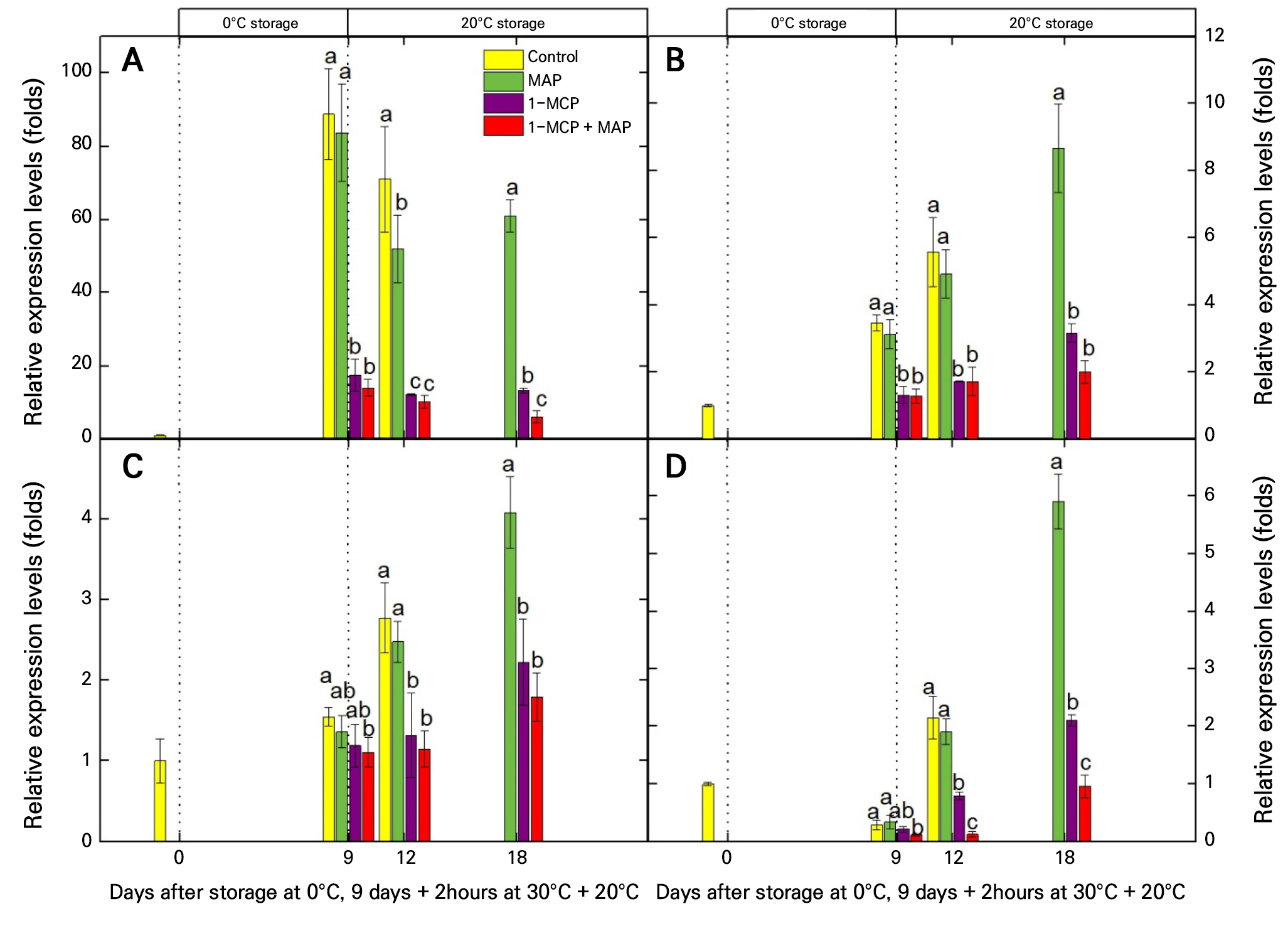
-
Effects of MAP and 1-MCP Treatments on the Quality of ‘Gampung’ Sweet Persimmon during a Simulated Marketing Period
MAP 및 1-MCP 처리가 모의 유통 과정 중 ‘감풍’ 단감 품질에 미치는 효과
-
Yeji Moon, Mi Hee Shin, Gyeong Ho Kim, Dong Ha Kim, Yun-Hee Kim, Kyeong Bok Ma, Byulhana Lee, Jin Gook Kim
문예지, 신미희, 김경호, 김동하, 김윤희, 마경복, 이별하나, 김진국
- In this study, we applied modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) to postharvest ‘Gampung’ persimmons to maintain their quality and extend …
본 연구는 수확 후 단감 ‘감풍’에 Modified Atmosphere Packaging(MAP)과 1-Methylcyclopropene(1-MCP)을 적용하여 국내 유통 및 수출 과정에서 품질 유지와 유통 기간 연장을 위한 …
- In this study, we applied modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) to postharvest ‘Gampung’ persimmons to maintain their quality and extend their distribution period during domestic distribution and export, aiming to develop better postharvest management techniques. The experiment included four groups: a no treatment group (Control) and treatment groups entitled MAP, 1-MCP, and 1-MCP + MAP. Simulated distribution conditions were based on the persimmon export process to Vietnam and consisted of nine days at 0°C (cold storage), two hours at 30°C, and 15 days at 20°C (room temperature storage), for a total of 24 days. Quality changes were evaluated after cold storage (before and after transport) and at three day intervals during room temperature storage. As a result, two MAP treatments (MAP and 1-MCP + MAP) showed prominent effects in reducing weight loss, with the 1-MCP + MAP treatment demonstrating the most significant effect. During the storage period, the expression levels of ethylene biosynthesis genes and genes related to cell wall modification were effectively suppressed in both 1-MCP-treated groups (1-MCP and 1-MCP + MAP). Notably, the 1-MCP + MAP treatment exhibited excellent ethylene production and fruit-softening inhibition effects. Overall, the 1-MCP + MAP treatment effectively suppressed weight loss and maintained fruit quality during the simulated export distribution process.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 수확 후 단감 ‘감풍’에 Modified Atmosphere Packaging(MAP)과 1-Methylcyclopropene(1-MCP)을 적용하여 국내 유통 및 수출 과정에서 품질 유지와 유통 기간 연장을 위한 수확 후 관리 기술을 개발하고자 수행되었다. 처리구는 무처리, MAP, 1-MCP, 1-MCP + MAP의 네 가지로 설정하였으며, 모의 유통 조건은 베트남으로의 단감 유통 과정을 참고하여 총 24일로 0°C에서 9일(저온저장), 30°C에서 2시간, 20°C에서 15일(상온저장)로 설정하였다. 저온저장 전후 각각 1회, 상온저장 3일 간격으로 과실 품질 변화를 조사하였다. 그 결과 MAP를 처리한 두 처리구(MAP, 1-MCP + MAP)에서 감모 억제 효과가 두드러졌으며, 특히 1-MCP + MAP 처리구에서 가장 우수한 감모 억제 효과가 나타났다. 저장 동안 에틸렌 생합성 유전자와 세포벽 분해 유전자의 발현은 1-MCP를 처리한 두 처리구(1-MCP, 1-MCP + MAP)에서 효과적으로 억제하였다. 특히 1-MCP + MAP 처리구에서 가장 우수한 에틸렌 생성 및 과실 연화 억제 효과가 나타났다. 종합적으로 1-MCP + MAP 처리구가 모의 유통과정에서 뛰어난 감모 억제 및 품질 유지 효과를 보였다.
-
Effects of MAP and 1-MCP Treatments on the Quality of ‘Gampung’ Sweet Persimmon during a Simulated Marketing Period
-
Research Article
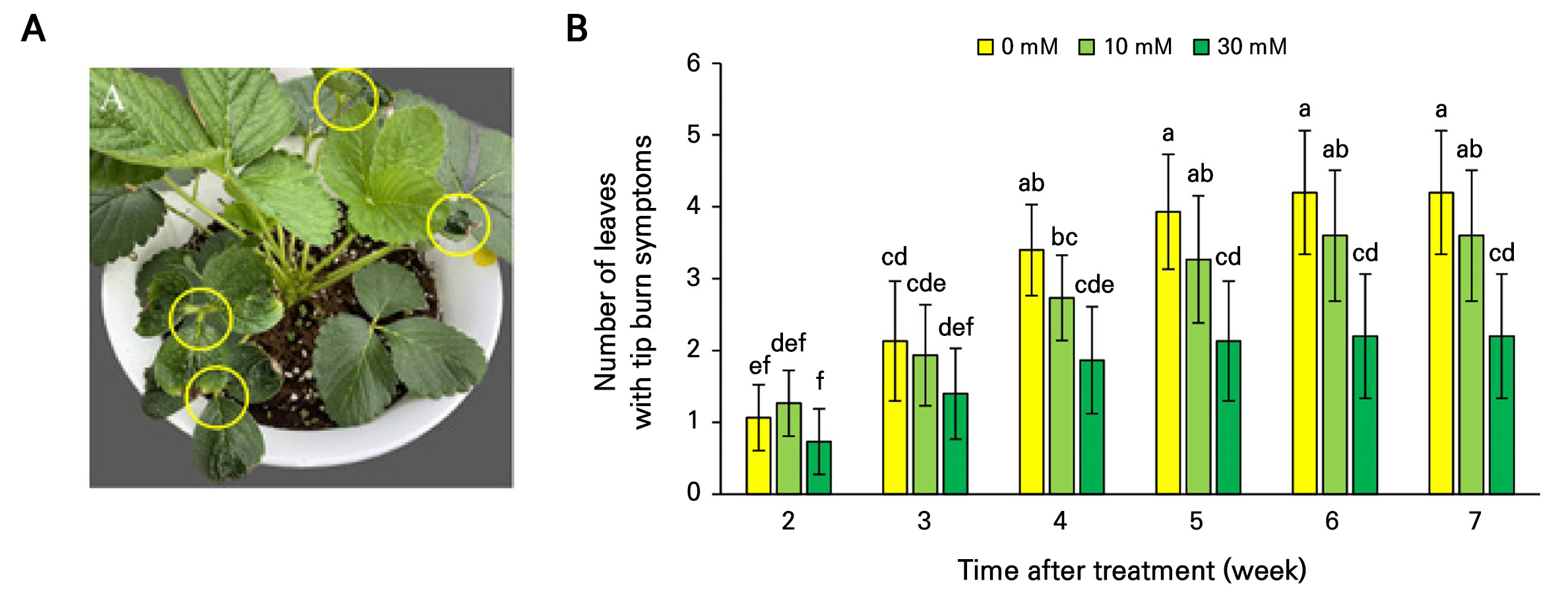
-
Effects of an Exogenous Trehalose Treatment on Ever-bearing Strawberry Cultivation during the High-Temperature Season
사계성 딸기 고온기 재배시 외인성 트레할로스 토양관주 처리의 효과
-
Jun-Hyung Lee, So Young Yi, Si-Yong Kang
이준형, 이소영, 강시용
- The hot and humid conditions during the summer in South Korea can hinder growth, and diseases become a factor as well with …
한국의 여름철 고온 다습한 환경은 딸기 생장에 장애를 주고 병해를 유발하여 생산성 및 품질 저하를 초래할 수 있다. 본 연구는 식물의 스트레스 …
- The hot and humid conditions during the summer in South Korea can hinder growth, and diseases become a factor as well with regard to reduced fruit productivity and lower quality of ever-bearing strawberry plants. This study explores trehalose, a non-reducing disaccharide known for its regulatory roles in plant stress responses, as an eco-friendly treatment to improve strawberry productivity under high-temperature conditions. Ever-bearing strawberries were irrigated with trehalose solutions at 0, 10, and 30 mM concentrations weekly for seven weeks. The results showed no significant differences in growth, fruit quality, or photosynthetic efficiency. However, trehalose affected soil conditions, with the soil electrical conductivity (EC) decreasing as the concentration of treated trehalose increased. By the fourth week, EC in the 30 mM treatment group was lower (0.94 dS·m-1) than in the control (1.56 dS·m-1). This trend suggests that trehalose improves the soil. Additionally, the trehalose treatment reduced leaf tip burn symptoms in a concentration-dependent manner. By week six, the 30 mM treatment group displayed fewer affected leaves (2.2 per plant) than the control group (4.2 leaves), showing nearly a 50% reduction. The findings here indicate that trehalose can improve the soil EC and mitigate leaf tip burn symptoms, enhancing plant resilience. This suggests the potential of trehalose as a sustainable treatment for managing stress during strawberry cultivation, warranting further explorations into broader agricultural applications of this disaccharide.
- COLLAPSE
한국의 여름철 고온 다습한 환경은 딸기 생장에 장애를 주고 병해를 유발하여 생산성 및 품질 저하를 초래할 수 있다. 본 연구는 식물의 스트레스 반응 조절에 중요한 역할을 하는 비환원성 이당류인 트레할로스 처리를 통한 고온 환경하 딸기 재배시에 스트레스 경감을 위한 친환경제제로서의 이용 가능성을 탐구하고자 하였다. 사계성 딸기 ‘W-331’ 를 여름철에 유리온실내에서 상토를 채운 포트에 재배하고, 0(대조구), 10, 30mM 농도의 트레할로스 용액을 매주 2L씩 7주간 관주하여 처리하였다. 연구 결과, 트레할로스 처리에 따른 딸기의 생장, 과일 품질 및 광합성 효율 등에는 유의미한 차이가 없었다. 그러나 트레할로스는 토양 상태에 영향을 미쳤으며, 트레할로스 농도가 증가할수록 토양 전기전도도(EC)가 감소하는 경향을 보였다. 4주차에는 30mM 농도의 처리군에서 EC 값이 대조구(1.56dS·m-1)에 비해 낮은 0.94dS·m-1을 기록했다. 이는 트레할로스가 토양 물리적 특성 개선에 기여할 수 있음이 시사되었다. 또한, 트레할로스 처리에 의해 딸기 잎끝마름 증상이 농도 의존적으로 감소하였으며, 6주차에는 30mM 처리군에서 잎끝마름 증상을 보인 잎 수가 대조구(4.2개)에 비해 약 50% 감소한 2.2개로 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 트레할로스 30mM를 관주처리하면, 토양 EC를 개선하고 잎끝마름 증상을 완화시켜 식물의 내성 향상에 기여할 수 있고, 시들음병 증상을 완화하는 것을 나타낸다. 따라서 트레할로스 처리가 딸기 재배에서 고온 스트레스 경감을 위해 활용될 수 있는 것으로 보여져, 향후 구체적인 작용 기작 구명과 활용 방안 연구가 필요하다고 생각된다.
-
Effects of an Exogenous Trehalose Treatment on Ever-bearing Strawberry Cultivation during the High-Temperature Season


 Horticultural Science and Technology
Horticultural Science and Technology










