About This Journal
Horticultural Science and Technology (abbr. Hortic. Sci. Technol., herein ‘HST’; ISSN, 1226-8763), one of the two official journals of the Korean Society for Horticultural Science (KSHS), was launched in 1998 to provide scientific and professional publication on technology and sciences of horticultural area. As an international journal, HST is published in English and Korean, bimonthly on the last day of even number months, and indexed in ‘SCIE’, ‘SCOPUS’ and ‘CABI’. The HST is devoted for the publication of technical and academic papers and review articles on such arears as cultivation physiology, protected horticulture, postharvest technology, genetics and breeding, tissue culture and biotechnology, and other related to vegetables, fruit, ornamental, and herbal plants.



-
Review
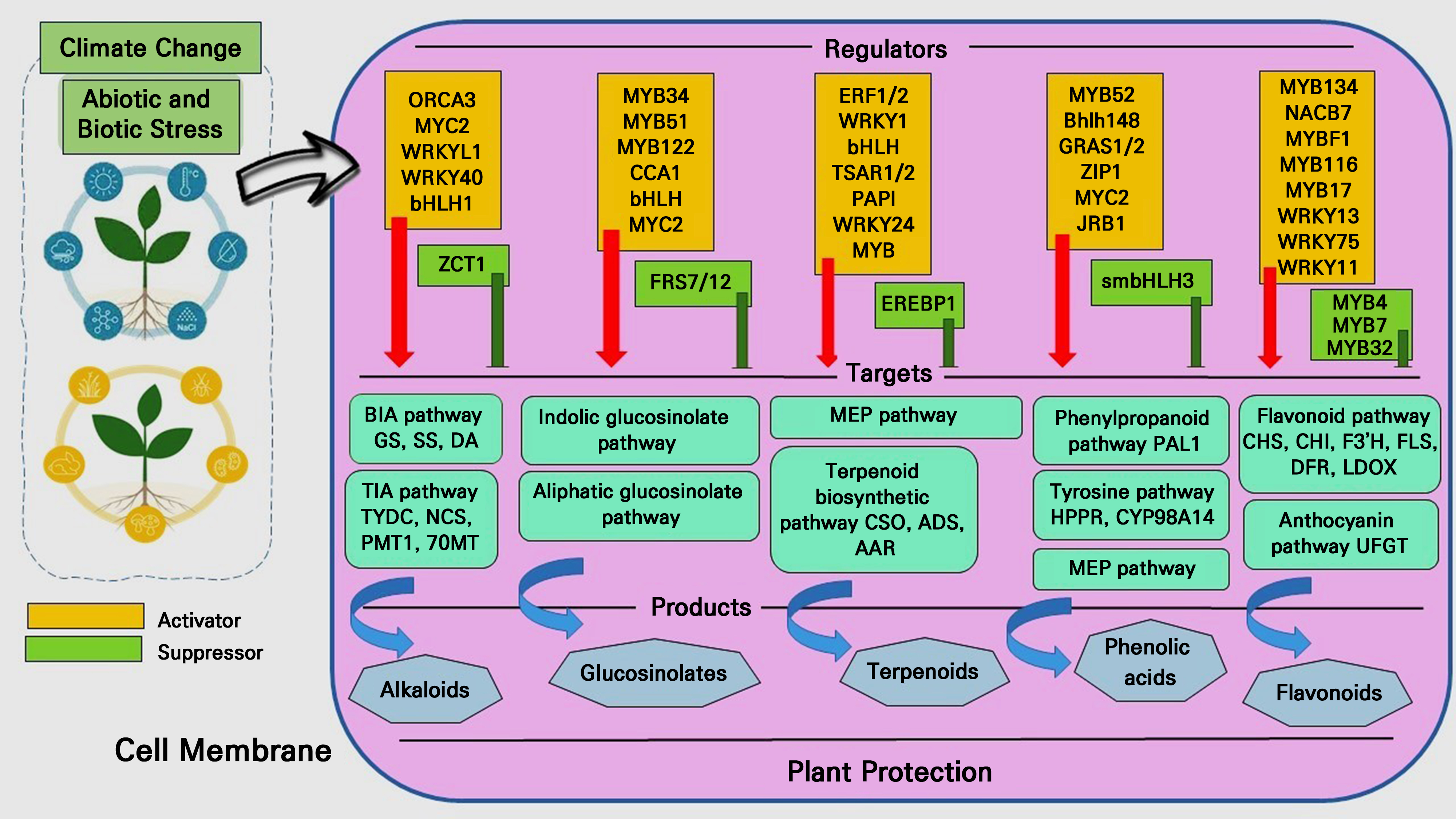
- Recent Understanding of Functional Genomics for Horticultural Plant Secondary Metabolites Biosynthesis under Climate Change
- Muhammad Anas, Shan-Shan Qi, Dao-Lin Du, Zhi-Cong Dai
- Horticultural plants synthesize secondary metabolites which are crucial for environmental adaptability, pollination, development regulation, and defense against diseases and herbivores. Plants respond …
- Horticultural plants synthesize secondary metabolites which are crucial for environmental adaptability, pollination, development regulation, and defense against diseases and herbivores. Plants respond to environmental stress through complex mechanisms, including gene expression and secondary metabolite synthesis. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind plant secondary metabolite generation is essential for sustainable agriculture and for protecting natural ecosystems as well. Climate change threatens plants in areas with significant biodiversity, and recent advancements in metabolite detection and identification have made it easier to study plant metabolism engineering. Genetic engineering can modify anthocyanin and flavonoid pathways to enhance pharmaceutical production. Functional genomics methods, such as metabolomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics, can be utilized to gain knowledge of biological systems. Stress reactions are influenced by post-transcriptional regulation, with the WRKY transcription factor family regulating defense-related secondary metabolite biosynthesis through inducible expression patterns. BHLH transcription factors govern the production of chemicals that inhibit stress. Examples include anthocyanins, alkaloids, glucosinolates, diterpenoid phytoalexins, and saponins. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind plant secondary metabolite generation is crucial for protecting natural ecosystems and promoting sustainable agriculture. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
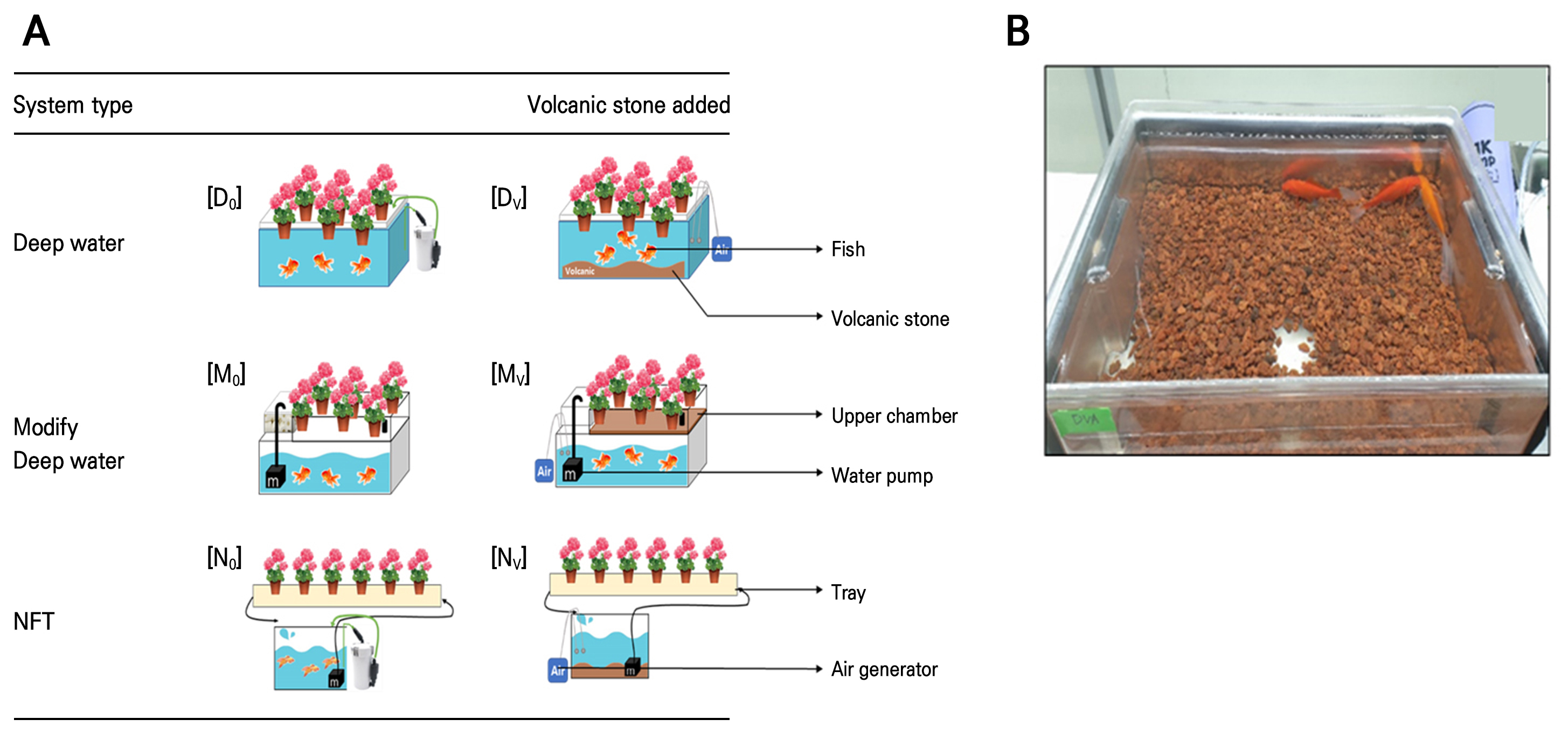
- Effect of Different Aquaponic Systems and Presence of Volcanic Stone Filtering Material on Nutrient Concentration in Water and Geranium Growth
- Hyoun-Jin Lee, Minkyung Kim, MG Rabbani, Seoa Yoon, Eunyoung Choi, Yeo Joong Yoon, Ki Young Choi
- Aquaponics combines hydroponic cultivation and aquaculture, where water quality is a primary consideration for both plant growth and fish health. In many …
- Aquaponics combines hydroponic cultivation and aquaculture, where water quality is a primary consideration for both plant growth and fish health. In many cases, the filtering material is helpful tool to maintain and optimize water quality for plant and fish. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of different types of aquaponic systems and the presence of volcanic stone as a filtering material on the water quality and the growth of geranium pot flower plants. Goldfish was used. The experiment was held in a controlled environment for six weeks, and three types of aquaponic systems were used: deep water culture (D), modified deep water culture (M), and nutrient film technique (N). Each type of system had two different settings, based on the presence of the volcanic stone filtering material (V). Hence, a total of six different treatments, D0, DV, M0, MV, N0, and NV, were used, where 0 and V indicate the absence and presence of volcanic stones in an aquaponic system, respectively. The results showed that NH4+ and NO3– concentrations of aquaponic water were increased in all treatments compared to their initial stage. After the treatment period, the concentrations of NO3– and K+ were higher in D0, M0, and N0 treatments compared to those where volcanic stones were present (DV, MV, and NV). However, after the treatment period, Ca2+ ions showed decreased concentration compared with their initial stage in all treatments, except M0 and MV. The EC level steadily increased in all treatments over time; at six weeks after treatment, it was around 0.4 dS·m-1 in all treatments. However, pH fluctuated during the treatment period. At six weeks after treatment, the plant height, leaf length, leaf width, and SPAD value of geranium plants were not significantly affected by the presence of volcanic stone in different types of aquaponic systems (D, M, and N). Nevertheless, the leaf area of the geranium was higher in N0 and NV treatments than in the others. Furthermore, total root length, total root surface area, and the number of root tips were higher in NV-treated plants. In addition, principal component analysis (PCA) analysis showed that the maximum growth parameters of plant responses were closer to the N0 and NV treatments. These results suggest that comparatively, treatment NV is preferable for maintaining sustainable water quality and the growth of geranium plants in an aquaponic system. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Polyploid and Doubled Haploids Induction in Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC. through Oryzalin Treatment-Mediated Chromosome Doubling
- Woo Seok Ahn, Tae Il Kim, Cheong A Kim, Woo Tae Park, Jin-Tae Jeong, Mok Hur, Jeonghoon Lee, Sung Ju Ahn, Yun Chan Huh, Sung Cheol Koo
- Through chromosome doubling in haploid regenerants derived from the microspore culture, doubled haploid (DH) homozygous lines were established within one to two …
- Through chromosome doubling in haploid regenerants derived from the microspore culture, doubled haploid (DH) homozygous lines were established within one to two generations. This process shortens the time required to produce homozygous plants compared to the time needed for conventional breeding methods, which require multiple generations of self-fertilization. In this study, we aimed to identify an optimal oryzalin concentration and duration of the treatment for chromosome doubling in Platycodon grandiflorum and develop a method for inducing DHs. Four different concentrations of oryzalin (12.5, 25, 50, and 100 mg·L-1) were applied for one to three days (once a day) to the shoot apical meristem of P. grandiflorum plants. The polyploid induction rate reached its highest (27.78%) when 50 mg·L-1 of oryzalin was applied for three days. The application of 50 mg·L-1 oryzalin for three days to haploids obtained via shed-microspore culture induced chromosome doubling, with a ploidy analysis confirming successful DH induction in 238 of 564 plants. These plants were then evaluated for their morphological traits to identify superior lines, followed by seed harvesting. Thus, we established a technique for inducing polyploids and DHs in P. grandiflorum by means of an oryzalin treatment. This method can be applied to P. grandiflorum and other medicinal plants for DH induction, facilitating the rapid development of homozygous lines and considerably reducing the breeding time. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Hibiscus syriacus ‘Samilhong’: A Novel Korean Cultivar with Enhanced Ornamental Traits and International Intellectual Property Protection
- Yoo Mi Ha, Kyung Ku Shim, Kyung Sub Yoon, Hyeyoung Choi, Ki Byung Lim
- The new Hibiscus syriacus cultivar ‘Samilhong’ was developed to address the growing demand for compact, refined ornamental shrubs suitable for contemporary urban …
- The new Hibiscus syriacus cultivar ‘Samilhong’ was developed to address the growing demand for compact, refined ornamental shrubs suitable for contemporary urban landscapes and container cultivation. Through controlled hybridization and successive selection, ‘Samilhong’ consistently exhibits a stable dwarf and compact growth habit, dense branching, and a well-proportioned canopy throughout its developmental stages, differentiating it from the paternal parent and control cultivar, ‘Samchulli.’ At five years of age, ‘Samilhong’ has a significantly reduced height (122.0 ± 5.7 cm) and a lower shape index (0.85 ± 0.09), indicative of restrained vertical growth and enhanced manageability. With regard to its leaf morphology, ‘Samilhong’ is characterized by longer, narrower leaves with more deeply lobed margins, contributing to fine-textured foliage. Distinctive floral characteristics comprise a smaller flower diameter, a more vivid and elongated red eye spot, and narrower, undulate petals with slight overlap (I-b), which collectively confer an intricate and graceful appearance compared with the compact floral form of ‘Samchulli.’ ‘Samilhong’ exhibits extended individual flower longevity of approximately 54 h, nearly three times that of ‘Samchulli,’ coupled with consistently prolific flower production. The new cultivar exhibits robust adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, including tolerance to heat, drought, and partial shade. It is readily propagated clonally via cuttings, maintaining genetic stability across generations. For the commercialization of ‘Samilhong’, plant variety protection in Korea was secured in 2015, European Community plant variety rights were granted in 2023, and a U.S. plant patent was approved in 2024. The cultivar has been introduced to the European market under the trade name ‘Little Legends Pink.’ This study records the first instance of a Korean-developed H. syriacus cultivar achieving simultaneous intellectual property protection in Korea, the United States, and Europe, thereby attesting to its substantial ornamental appeal, ecological resilience, and international market competitiveness as a premium cultivar for contemporary landscape applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
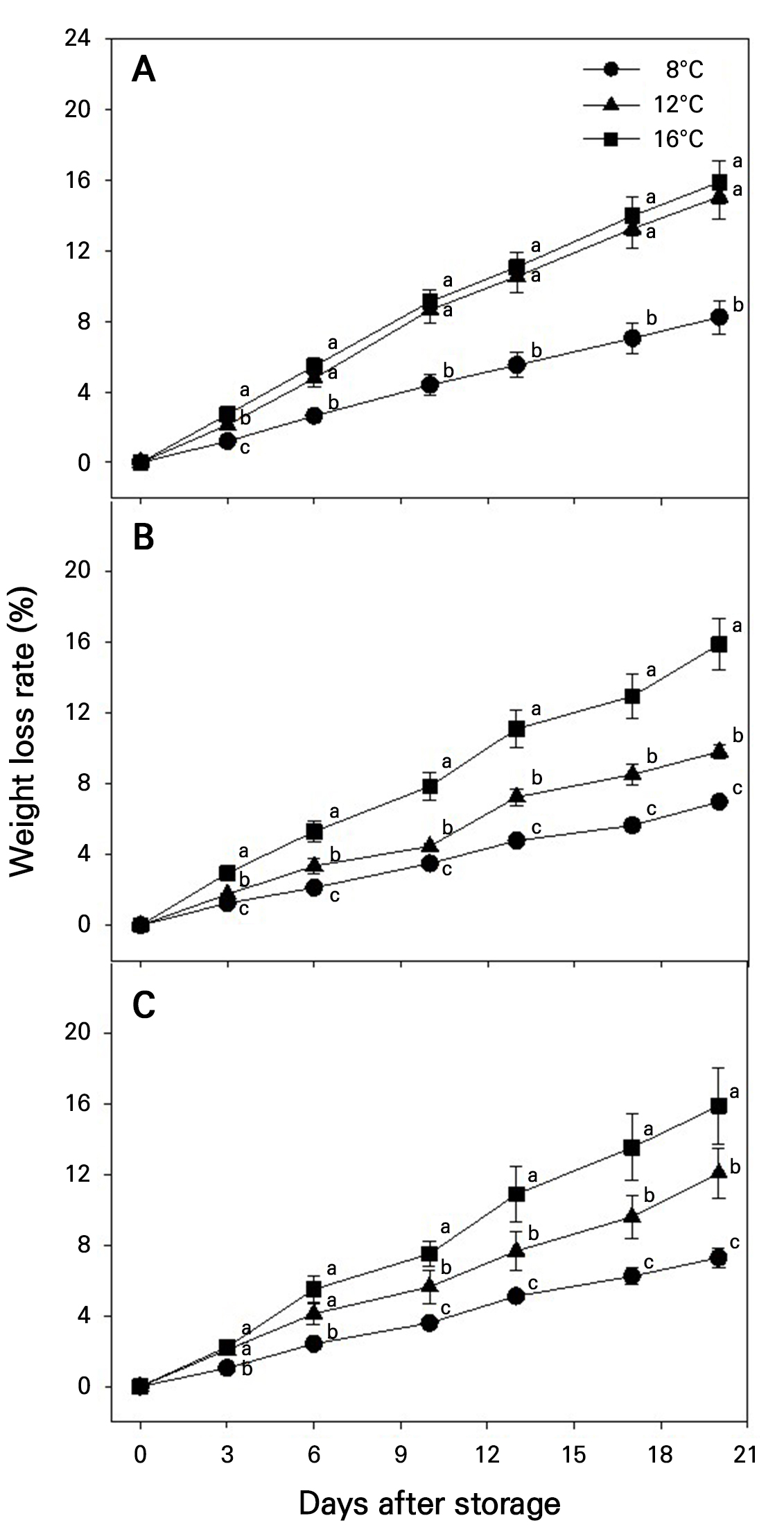
- Changes of Quality Attributes during Storage at Different Temperatures in ‘Irwin’ Mango Fruits Harvested at Three Maturity Stages
- Yeon Jin Jang, Seong Cheol Kim, Mockhee Lee, Misun Kim, Ha Rim Hong, Su Jin Kim, Sun Woo Chung, Kwan Jeong Song
- In temperate regions, greenhouse cultivation of mango (Mangifera indica L.) is expanding due to rising temperatures and improved horticultural techniques. The …
- In temperate regions, greenhouse cultivation of mango (Mangifera indica L.) is expanding due to rising temperatures and improved horticultural techniques. The red-blushed cultivar ‘Irwin’ is the dominant variety, valued for its consistent flowering and high market appeal. However, most fruits are harvested during the mid-summer peak season, leading to oversupply and price drops. To extend the marketability period, this study aimed to identify the optimal combination of harvest maturity and storage temperature to maintain postharvest quality outcomes. ‘Irwin’ mangoes grown in a greenhouse on Jeju Island were harvested at three different peel-color stages and stored at 8, 12, or 16°C. External (weight loss rate, shriveling, decay, peel color) and internal (SSC, TA, pH, firmness) quality traits were monitored at three-day intervals. Two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate the effects of the harvest stage and temperature as well as the interaction between these two variables. Among all traits, firmness showed the most pronounced response, decreasing with both an increase in the maturity stage and the storage temperature. SSC increased gradually during storage, while TA and firmness declined. The pH also rose over time, especially at higher temperatures and advanced maturity stages. Notably, shriveling symptoms appeared earlier in stage 1 fruit stored at 8°C, suggesting a potential injury due to chilling. Fruits harvested at stage 2 and stored at 8°C showed delayed ripening and maintained the best external quality. A clear quality gap was observed between 8°C and higher temperatures, while 12°C and 16°C showed minimal differences. These results suggest that harvesting at stage 2 and storing fruit at 8°C can effectively extend the shelf life and reduce market saturation during the summer peak, leading to improved postharvest management and better income stability for growers. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
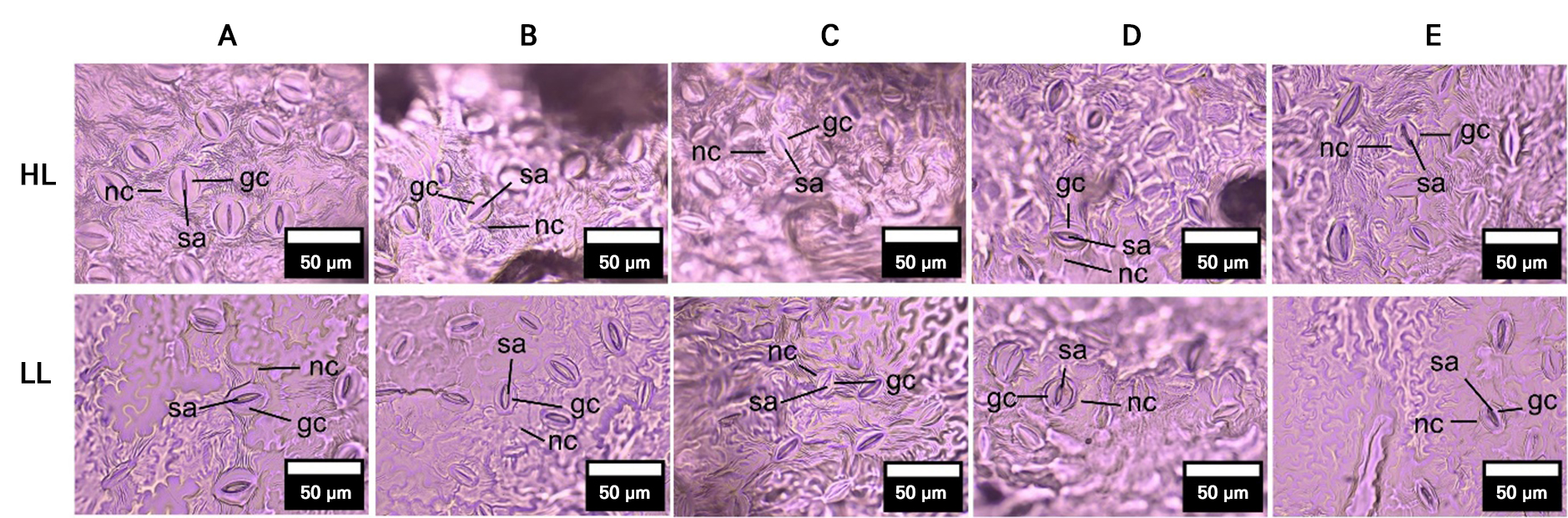
- Adaptability of Apple Varieties to Tropical Lowland Conditions: Anatomical and Ecophysiological Insights
- Lia Hapsari, Wasilatul Khoiroh, Sukartini, Agus Sugiyatno, Anang Triwiratno, Nirmala Friyanti Devy, Agus Sutanto, Hardiyanto
- This study investigates the adaptive responses of five apple varieties (‘Anna’, ‘Huanglin’, ‘Manalagi’, ‘Rome Beauty’, and ‘Royal Red’) by assessing leaf anatomical …
- This study investigates the adaptive responses of five apple varieties (‘Anna’, ‘Huanglin’, ‘Manalagi’, ‘Rome Beauty’, and ‘Royal Red’) by assessing leaf anatomical and ecophysiological traits under contrasting environments. The results reveal significant altitude-induced variations in leaf area, thickness, cuticle and epidermis structure, stomatal density, chlorophyll content, and specific leaf area (SLA). In lowland conditions, apple varieties developed smaller and thinner leaves, thicker cuticles, and epidermal layers to mitigate water loss under heat stress. ‘Royal Red’ and ‘Rome Beauty’ exhibited increased SLA, enhancing photosynthetic efficiency, while ‘Anna’ maintained both a thicker epidermis and cuticle for improved water retention. ‘Huanglin’ and ‘Manalagi’ adjusted by increasing the stomatal density to optimize gas exchange. A principal component analysis confirmed altitude-related differentiation in adaptive traits. The findings here offer valuable insights for breeding climate-resilient apple varieties suitable for tropical lowland cultivation under global warming scenarios. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Assessment of the Chemical Properties and Resource Utilization Potential of Paprika Plant Residues
- Se Hun Ju, Young Je Kim, Yoon Go, Eun Ji Kim, Jun Gu Lee, Jongseok Park, Daegi Kim, Beom Seon Lee, Haeyoung Na
- The area of hydroponic cultivation in Korea has rapidly expanded in recent years, raising concerns over the management of by-products, such as …
- The area of hydroponic cultivation in Korea has rapidly expanded in recent years, raising concerns over the management of by-products, such as waste plant residues and spent growing media. Despite the increase in hydroponic cultivation, studies of the treatment and recycling of plant residues and growing media remain limited, necessitating the development of sustainable disposal and utilization methods. This study aims to evaluate the chemical characteristics of paprika plant residues generated after hydroponic cultivation and assess their potential for conversion into solid fuels, thereby proposing sustainable utilization strategies. Plant residues were collected from six farms across the country and analyzed for pesticide residues, heavy metals, inorganic components, and for their solid fuel quality. The analysis revealed that certain pesticide residues exceeded the permissible limits set by domestic and international standards, with zinc (Zn) levels also surpassing the acceptable thresholds in some samples. Conversely, the residues contained high levels of essential inorganic nutrients such as nitrogen (N), calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and magnesium (Mg), indicating their potential for use as compost or soil amendments. Although the lower heating value, moisture content, and ash content of the residues did not meet the standard solid fuel quality criteria, the high biomass content suggests that they could be effectively utilized as solid fuel with additional pre-drying treatments. These findings indicate that paprika plant residue, when properly pretreated and managed, can be repurposed using various resource recovery methods, thereby contributing to agricultural waste reduction and the development of sustainable agricultural systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
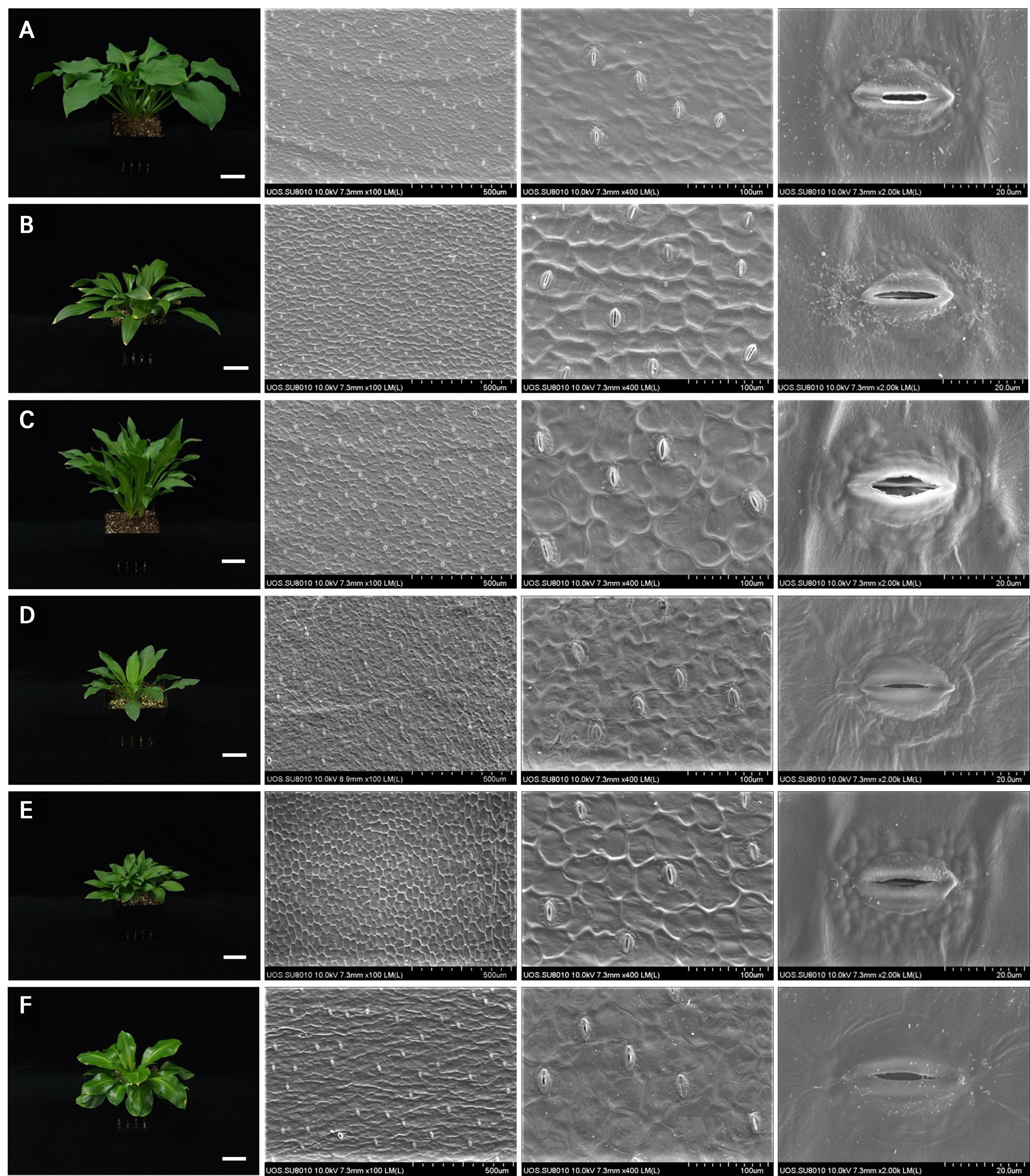
- Interspecific Variation in Stomatal Traits among Six Korean Hosta Species
- Bo Kyeong Kang, Wan Soon Kim
- Although numerous Hosta cultivars have been developed for horticultural purposes, the growing attention to wild Hosta species under climate change highlights the …
- Although numerous Hosta cultivars have been developed for horticultural purposes, the growing attention to wild Hosta species under climate change highlights the need to evaluate their ornamental value and ecological adaptability. Among various morphological features, stomatal characteristics play a pivotal role in plant responses to environmental stressors. The present study investigated six Korean Hosta species (H. capitata, H. clausa, H. jonesii, H. minor, H. venusta, and H. yingeri) to establish foundational data on interspecific variation in leaf-level adaptive traits. All of the taxa exhibited an anomocytic stomatal type characterized by the absence of distinct subsidiary cells surrounding the guard cells. Despite this shared morphology, substantial differences were observed in the stomatal dimensions and frequency; H. yingeri displayed the largest guard cells (up to 1.24-fold), whereas H. clausa had the highest stomatal density (up to threefold), accompanied by the smallest size. A significant negative correlation was found between the stomatal size and density (r = –0.61***). Principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) revealed discrete groupings based on stomatal traits, with H. clausa and H. yingeri forming separate clusters. These findings provide critical baseline information for interpreting interspecific differences in habitat preferences, foliar morphologies, and adaptive strategies among Korean Hosta species. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
-
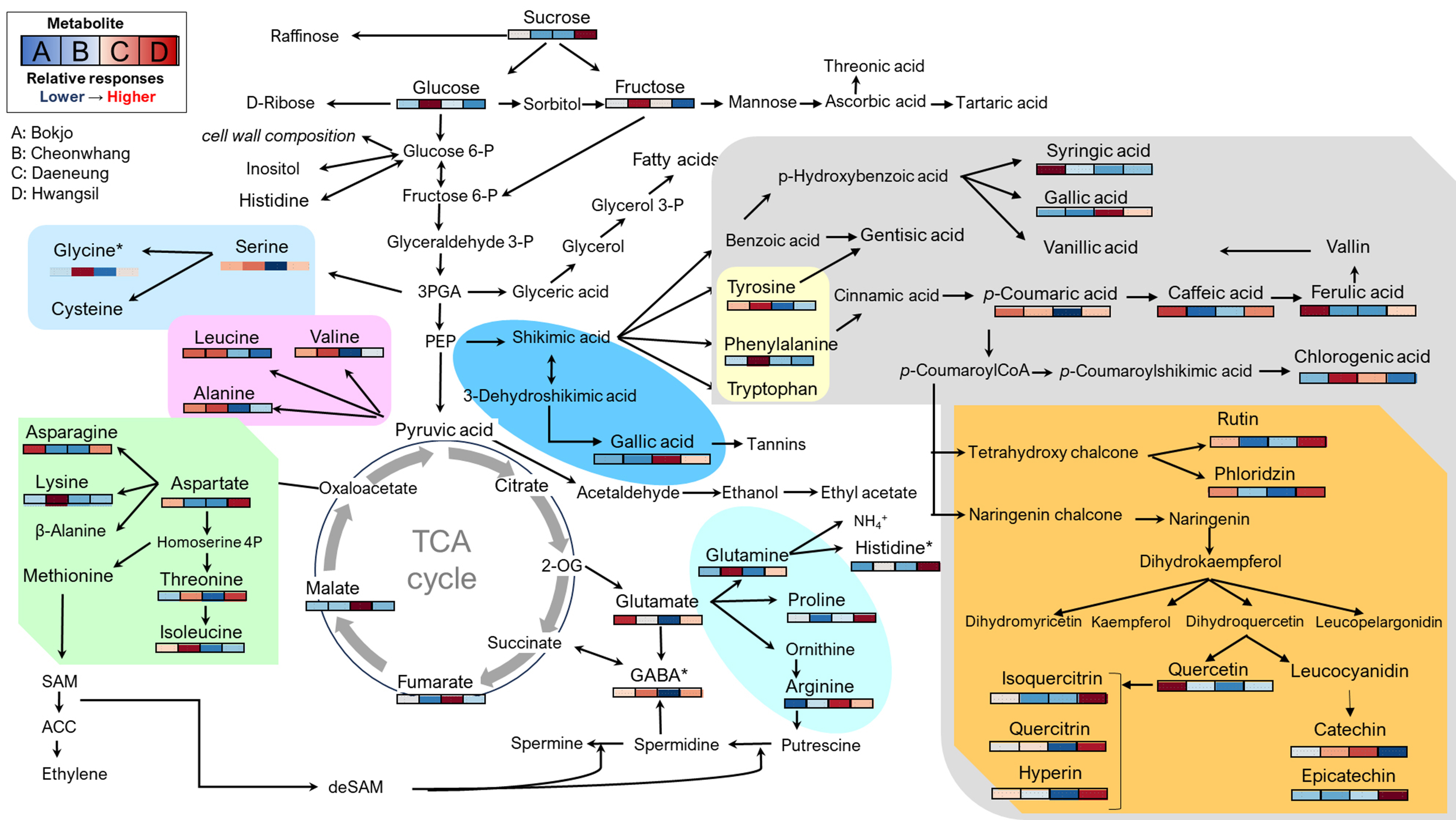
Comparison of Metabolite Levels and Antioxidant Activity between Dried Fruits of the Korean Traditional ‘Bokjo’ and Three Large-sized Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) Cultivars
한국 재래종 ‘복조’와 왕대추 3 품종 간 건조 열매의 대사산물 함량 및 항산화 활성 비교
-
MiAe Cho, Chang Moo Lee, Uk Lee, Jinwook Lee, Hnin Phyu Lwin, Dong-Shin Kim, Jong Cheol Park
조미애, 이창무, 이욱, 이진욱, 히닌퓨 르원, 김동신, 박종철
- The cultivated area of large-sized Ziziphus jujuba Mill., commonly known as wang jujube in South Korea, is undergoing an expansion due to …
왕대추(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)는 생과용 과일이라는 인식의 확산으로 재배면적이 확대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 한국 재래종 ‘복조’와 왕대추 품종 간 건조된 과일에서의 대사체 …
- The cultivated area of large-sized Ziziphus jujuba Mill., commonly known as wang jujube in South Korea, is undergoing an expansion due to the increasing recognition of its value as a fresh fruit. This study aimed to analyze differences in metabolites and antioxidant activities between the dried fruits of Korean ‘Bokjo’ landrace and three cultivars of large-sized jujube as part of an effort to evaluate the potential use of wang jujube as a medicinal material and food ingredient. The sugar content was highest in the Cheonhwang, Daeneung, Hwangsil, and Bokjo cultivars, in descending order, while the organic acid content was highest in Daeneung, followed by Cheonhwang, Bokjo, and Hwangsil. The levels of minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids were most abundant in Bokjo, followed by Hwangsil, Daeneung, and Cheonhwang. Phenolic compounds were most abundant in Bokjo, Daeneung, Hwangsil, and Cheonhwang, with rutin and quercetin being predominant in Bokjo, Cheonhwang, and Hwangsil, while Daeneung mainly contained rutin and gallic acid. A principal component analysis revealed that the three large-sized jujube cultivars were compositionally distinct from the traditional Bokjo variety, forming two separate groups: the ‘Bokjo-Hwangsil’ group and the ‘Cheonhwang-Daeneung’ group. The overall DPPH antioxidant activity ranged from 66.5 to 70.7%, showing minimal differences across cultivars. The ABTS antioxidant activity ranged from 68.3 to 69.2%, showing no significant variation. Positive correlations were observed between the antioxidant activity and several compounds, in this case palmitic acid, phloridzin, acetic acid, aspartic acid, palmitoleic acid, copper, stearic acid, total flavonoids, calcium, sucrose, hyperin, and potassium. In conclusion, while there were differences in the metabolite composition among the four cultivars, their antioxidant activities showed some similarities. These findings suggest that dried fruits of the Hwangsil, Daeneung, and Cheonhwang cultivars can potentially find uses as medicinal and functional food ingredients. However, further research is necessary to elucidate how compositional differences influence biological efficacy in these cultivars.
- COLLAPSE
왕대추(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)는 생과용 과일이라는 인식의 확산으로 재배면적이 확대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 한국 재래종 ‘복조’와 왕대추 품종 간 건조된 과일에서의 대사체 및 항산화 활성 차이를 비교 분석하여, 왕대추의 약재와 식재료로의 이용성을 검토하고자 하였다. 네 품종의 구성 성분으로 유리당은 ‘천황’, ‘대능’, ‘황실’, ‘복조’ 순, 유기산은 ‘대능’, ‘천황’, ‘복조’, ‘황실’ 순으로 높았으며, 미네랄, 아미노산과 지방산은 ‘복조’, ‘황실’, ‘대능’, ‘천황’ 순으로 높았다. 개별 페놀성분은 ‘복조’, ‘대능’, ‘황실’, ‘천황’ 순으로 함유되어 있었는데, ‘복조’, ‘천황’ 및 ‘황실’ 품종에는 rutin과 quercetin이 주로 함유되어 있었고, ‘대능’에는 rutin, gallic acid가 주로 함유되어 있었다. 주성분 분석을 통하여 왕건대추 세 품종은 재래종인 ‘복조’와는 거리가 있는 구성 성분을 함유하는 것으로 나타났고, ‘복조’–‘황실’ 그룹과 ‘천황’–‘대능’ 그룹으로 나뉘었다. 네 품종간 항산화 활성 비교 시, DPPH 항산화 활성은 약 66.5–70.7%, ABTS 항산화 활성은 약 68.3–69.2%로 활성 차이는 크지 않았다. 항산화 활성에는 palmitic acid, phloridzin, acetic acid, aspartic acid, palmitoleic acid, Cu, stearic acid, palmitoleic acid, 총 플라보노이드, Ca, sucrose, hyperin, K 등이 높은 양의 상관관계를 보였다. 건대추 네 품종의 대사산물 함량은 각각 구성에 차이가 있으나 항산화 활성은 큰 차이가 없어 왕대추인 ‘황실’, 대능, ‘천황’ 품종의 건대추도 약용 및 기능식품으로 이용할 수 있을 것으로 보인다. 다만 품종간 구성 성분간 차이가 효능에 어떤 차이를 보일지에 대해서는 보다 세밀한 연구가 필요하다.
-
Comparison of Metabolite Levels and Antioxidant Activity between Dried Fruits of the Korean Traditional ‘Bokjo’ and Three Large-sized Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) Cultivars
-
Research Article
-
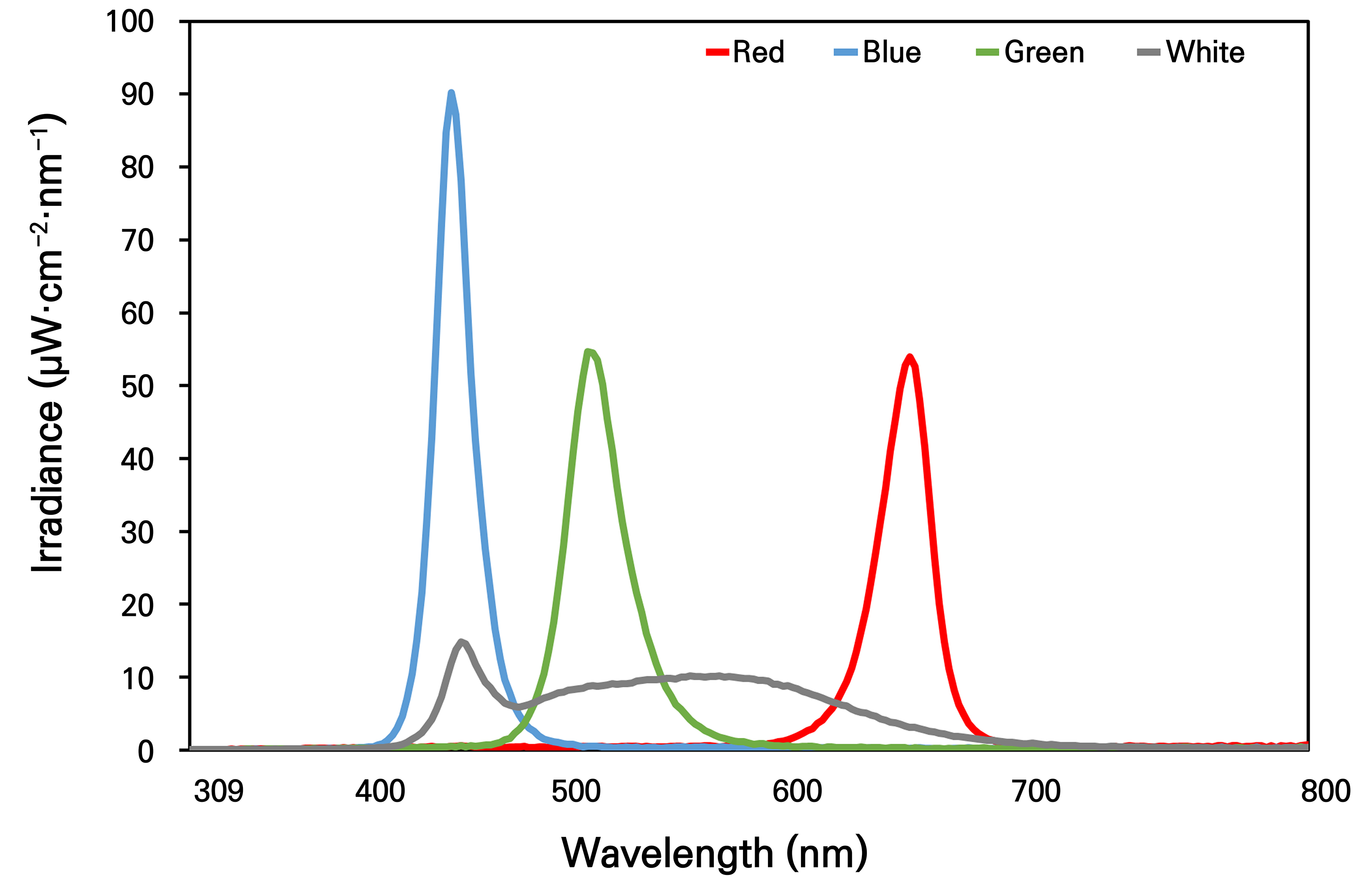
Anti-inflammatory Activity of Sprouts according to Hydro-priming and Light Quality Levels in Vigna vexillata (L.) A.Rich. var. tsusimensis Matsum. Seeds
돌동부 종자의 수화프라이밍과 광질처리에 따른 새싹의 항염 활성
-
Sae Rom Kim, Kyungtae Park, Hamin Lee, Bo-Kook Jang, Ju-Sung Cho
김새롬, 박경태, 이하민, 장보국, 조주성
- This study was performed to confirm the optimal conditions for the germination and production of high-functional sprouts of Vigna vexillata (L.) A.Rich. …
본 연구는 자생식물이자 약용식물로 알려진 돌동부 종자의 발아특성 및 고기능성 새싹생산을 위한 최적조건을 구명하기 위해 수행하였다. 돌동부 종자의 길이는 5.83mm, 너비는 4.08mm, …
- This study was performed to confirm the optimal conditions for the germination and production of high-functional sprouts of Vigna vexillata (L.) A.Rich. var. tsusimensis Matsum. seeds known to be a native, medicinal plant in Korea. The seed length and width were respectively 5.83 mm and 4.08 mm, the weight of 1,000 seeds was 51.08 g, and the seed viability rate was 80.0%. Seed germination was highest at 30°C under light conditions and at 25°C under dark conditions, and germination tended to be inhibited regardless of the light condition at 15°C. It was confirmed that as the germination percentage (GP) increased, T50 and mean germination time were shortened, with germination rate increasing as the temperature was increased under light conditions. The effect of separation was confirmed by distinguishing absorbed seeds and unabsorbed seeds according to soaking period and temperature. The difference in GP between absorbed seeds (64%) and unabsorbed seeds (15%) was 49%, which had the effect of seed separation. We considered the optimal soaking treatment to be two days at 15°C to separate non-dormant seeds and to produce sprouts. When seeds were hydro-primed according to the light quality by applying optimal immersion conditions, GP was excellent in blue light, and sprout growth was excellent in all light quality conditions. Sprout extract had the best antioxidant content and activity under the blue light treatment and had the best NO production inhibition effect under the red light treatment.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 자생식물이자 약용식물로 알려진 돌동부 종자의 발아특성 및 고기능성 새싹생산을 위한 최적조건을 구명하기 위해 수행하였다. 돌동부 종자의 길이는 5.83mm, 너비는 4.08mm, 1,000립중은 51.08g였으며, 종자 활력은 80.0%이었다. 발아율은 명조건의 30°C, 암조건의 25°C에서 가장 높았고, 15°C에서 광조건 관계없이 발아가 억제되는 경향이었다. 돌동부 종자는 명조건에서 온도가 높아질수록 발아율이 증가하였고, T50과 평균발아일수는 단축하였으며, 발아속도는 높아지는 것으로 확인하였다. 종자 침수 온도와 기간에 따라 흡수종자와 비흡수종자를 선별하였으며, 흡수종자의 발아율(64%)은 비흡수종자(15%)와의 차이가 49%로 선별 효과가 있었다. 흡수종자의 발아율과 새싹의 생육을 비교하였을 때, 15°C의 2일 침수처리가 최적조건으로 판단된다. 침수 최적 조건을 적용하여 종자에 광질별 hydro-priming처리하였을 때 발아율은 청색광이 우수하였으며, 무처리구 대비 모든 광질에서 발아 및 초기생육이 우수하였다. 광질별 hydo-priming처리 후에 재배된 새싹 추출물은 청색광에서 항산화 함량 및 활성이 가장 우수하였으며, 적생광에서 NO 생성 억제효과가 가장 우수하였다.
-
Anti-inflammatory Activity of Sprouts according to Hydro-priming and Light Quality Levels in Vigna vexillata (L.) A.Rich. var. tsusimensis Matsum. Seeds


 Horticultural Science and Technology
Horticultural Science and Technology








